Vasculitis Treatment in Pelican Bay - Naples, FL
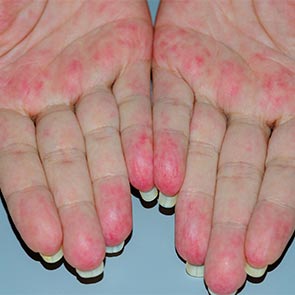
Vasculitis refers to a group of diseases that cause the inflammation of your blood vessels or blood vessel walls.
Inflammation is the body's response to injury, including injury to the blood vessels, and may cause pain, redness, warmth, swelling, and loss of function in the affected tissues.
In vasculitis, inflammation can lead to serious problems if ignored. Complications depend on which blood vessels, organs, or other body systems are affected.
There are many types of vasculitis, each with its own symptoms. Since its symptoms mimic those of many other medical conditions, getting medical attention is crucial.
Your healthcare provider can diagnose or rule out vasculitis and other underlying health concerns with blood tests and CT scans. To speak with a vasculitis specialist today in Pelican Bay - Naples, call (941) 845-6555 or contact Dr. Nancy Vance online.
What Are the Symptoms of Vasculitis?
The general symptoms of vasculitis include:
- fatigue or weakness
- weight loss
- rashes
- muscle pain
- headache
- lightheadedness
- fever
- joint pain
- night sweats
- nerve problems that cause numbness or weakness in your arms or legs
- shortness of breath (if your lungs are affected)
When blood vessels are inflamed, they might weaken, stretch, increase in size, or narrow (sometimes to the point of completely closing).
Other complications of these include:
- organ damage
- blood clots and aneurysms
- infections
- congestive heart failure
- seizures
- strokes
- kidney failure
Various types of vasculitis cause specific symptoms:
Giant cell arteritis
Also called temporal arteritis, this type inflames the arteries in your temples, causing scalp tenderness, jaw pain, blurry vision and blindness (rarely).
Cryoglobulinemia
Cryoglobulinemia vasculitis is caused by abnormal proteins in your blood, this condition cause joint pain and weakness, numbness, or tingling in in your arms or legs.
Behcet's disease
This type inflames your veins and arteries, causing mouth and genital ulcers, eye inflammation, and skin lesions that resemble acne.
Buerger's disease
This causes inflammation and blood clots in your hands and feet's blood vessels, resulting in pain and ulcers. In rare cases, it can affect the blood vessels in your heart, brain, and abdomen.
Hypersensitivity vasculitis
Also called allergic vasculitis, its primary symptom is red spots on your lower legs.
Kawasaki disease or mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome
This usually affects children under five and causes fever, rashes, and eye redness.
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
This type inflames the blood vessels of your throat, nose, sinuses, lungs, and kidneys, causing nasal congestion, sinus infections, and nosebleeds. Symptoms of granulomatosis with polyangiitis usually don't occur until the damage is advanced.
Polyarteritis nodosa
Inflames the blood vessels in your kidneys, digestive tract, skin, and nerves, causing rashes, weight loss, joint and muscle pain, abdominal pain after eating, high blood pressure, and kidney problems.
Henoch-Schonlein purpura
More common in children than in adults, it inflames the smallest blood vessels in your skin, joints, digestive tract, and kidneys, causing abdominal pain, bloody urine, joint pain, and a lower-leg rash.
Takayasu's arteritis
Affects your larger arteries (including those leading to your heart), causing weak pulse, high blood pressure, appetite loss, and blurry or double vision.
Microscopic polyangiitis
This affects small blood vessels in your kidneys, lungs, or nerves, causing abdominal pain, rashes, muscle pain, and weight loss. If your lungs are affected, you may cough up blood.
Churg-Strauss syndrome
Churg-Strauss syndrome is a rare condition that affects your lungs, kidneys, skin, heart, and limb nerves, causing skin changes, nerve pain, nasal allergies, and asthma.
What Causes Vasculitis?
The exact causes of Vasculitis aren't known. Some types may be related to genetics, and The Vasculitis Foundation reports that research shows Vitamin D deficiency may be a culprit.
Risk factors may contribute to getting vasculitis include smoking, hepatitis B and C, and autoimmune diseases like lupus.
Some types are caused by the immune system attacking healthy blood cells. Causes of this immune system attack include:
- reactions to certain medications, especially in hypersensitivity vasculitis
- blood cancers like lymphomas and multiple myeloma
- immune system diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus , or scleroderma
- infections like hepatitis B and C
How Is Vasculitis Diagnosed?
To diagnose vasculitis, your medical provider will examine you and discuss your medical history and any medications you're taking. You'll likely undergo tests to diagnose or rule out vasculitis and other underlying conditions, such as a biopsy:
- blood tests : to look for signs of inflammation (such as a high level of C-reactive protein), red blood cell count), and to detect antibodies
- urine test: to determine red blood cell count and protein
- imaging: x-rays, ultrasound, CT (computerized tomography), MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), and PET (positron emission tomography) help determine which blood vessels and organs are affected
- angiography: a thin, flexible tube is inserted into a large artery or vein that injects a dye that allows your blood vessels to better appear on an x-ray
How Is Vasculitis Treated?
Successful treatment centers on controlling the inflammation to resolve the underlying cause.
Moderate exercise - walking, stretching, swimming or cycling - can help to manage symptoms like joint pain and depression. People who are overcoming autoimmune health problems and dealing with fatigue usually need eight or more hours of sleep each night.
Nutritional supplements may have contraindications with pharmaceuticals. Always consult with your healthcare provider to make sure your treatments do not overlap and cancel out each other's effects.
Nutritional and herbal supplements
Since 70% of your immune system is in your gut-associated lymphoid tissue, nutritional intake can treat vasculitis.
- vitamin D supplements: deficiency has been shown to weaken immune system, skeletal system, and mental health; overdose can cause weakness, fatigue, sleepiness, headache, appetite loss, dry mouth, metallic taste, nausea and vomiting
- turmeric: strengthens your immune system and treats vasculature skin infections; side effects include nausea, dizziness, diarrhea, or infertility
- calcium supplements: protect your bone density during long-term steroid use; minor side effects include belching or gas, overdose may increase heart attack risk
- hawthorn: a herb that can heal vasculature damage; side effects include nausea, headache, fatigue, sweating, dizziness, palpitations, nosebleeds, insomnia, agitation
- ginger tea: this spice can help alleviate abdominal pain; side effects include heartburn, diarrhea, general stomach discomfort, and extra menstrual bleeding
- cayenne pepper: its antioxidants can relieve skin pain and swelling; may cause upset stomach, sweating, and skin irritation
- apple cider vinegar: balances PH level of digestive tract; side effects include delayed stomach emptying, decreased appetite, bone loss, throat burns, and skin burns
- lavender oil: massaging this herb can treat inflammation; may cause irritation, and may cause hormonal imbalance in protuberant boys
- diluted rosemary oil: massaging this herb can treat inflammation; large amounts can cause vomiting, uterine bleeding, kidney irritation, increased sun sensitivity, and skin redness
- frankincense oil: massaging this plant resin can treat inflammation; may cause irritation
- raw garlic: has antiviral properties; may cause burns when applied to children's skin
- holy basil: has healing properties
These nutritional treatments may have contraindications with the following conditions: pregnancy, breast feeding, bleeding disorders, smoking, surgery, diabetes , gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) , breast or ovarian cancer, gallbladder issues, iron deficiency, low blood pressure, certain allergies like to aspirin or cobalt, seizures, low acid levels in the stomach (achlorhydria), hyperphosphatemia, hypophosphatemia, abnormal or high red blood cell count, atherosclerosis, tuberculosis, hypothyroidism , hyperparathyroidism, Leber's disease, sarcoidosis and histoplasmosis.
An anti-inflammatory diet includes eating whole, unprocessed foods that are low in salt/sodium. These include:
- apples
- carrots
- brown or wild rice
- oatmeal
- dried beans and peas like kidney beans and black-eyed peas
- eggs
Electrolytes regulate nerve and muscle function and help rebuild damaged tissue. Foods that are rich in electrolytes like potassium and magnesium include:
- leafy green veggies
- bananas
- avocado
- sweet potato
- almonds
- yogurt/kefir
- black beans
- coconut water or milk
Foods to avoid include those that are difficult to digest or increase the odds of negative reactions for patients with weak immune systems, such as:
- gluten
- excess sugar and sweetened drinks
- conventional dairy
- processed meats
- undercooked meat or raw seafood
- coffee
- alcohol
Speak with your healthcare provider before drastically changing your diet.
Pharmaceutical medication
The type and duration of any prescription will depend on which organ is infected, and on severity of vasculitis. These drugs are used to control inflammation and to prevent relapse.
Some patients recover, others relapse and chose to stay on these medications permanently:
Corticosteroids
These drugs help control inflammation; commonly prescribed corticosteroids include the glucocorticoids prednisone and methylprednisolone.
Common side effects include weight gain, diabetes, and osteoporosis (bone thinning); Studies have shown that glucocorticoids for giant cell arteritis leads to significant toxicity in over 80% of the patients.1 Steroids for long-term use are often prescribed at the lowest possible dose to avoid or minimize side effects and potential addiction.
Steroid-sparing
These drugs ¬ including methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate, or cyclophosphamide – help control inflammation and reduce steroid dosage faster (tapering). Side effects include nausea, vomiting, fainting, dizziness, skin rashes, and anemia.
Biologic
Biological drugs like rituximab and tocilizumab suppress your immune system and can improve your motor functions. These drugs can cause side effects like nausea, dizziness, fatigue, fever, respiratory infections, and others.
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy
Unlike steroids – single chemical immune suppressors that basically turn off the immune system – MSCs help regenerate it. Promising studies show they can also signal a cell nucleus to turn off the inflammation response once it's no longer needed.2
MSCs originate in our small blood vessels where they control contraction and dilation. When they detect a vessel contracting or widening, MSCs measure damage and inflammation signals, order the cells in the area to repair damage, divide and replace missing cells, increase blood flow to damaged area and alter the behavior of our body's chief immune cells (T-Cells).
Surgery
In severe cases surgery can unblock arteries and remove bulges caused by aneurysms. To clear the arteries, two procedures include:
- endarterectomy: an incision is made into the artery, clamps are placed above and below the narrowing, and the plaque is removed, your surgeon enlarges the artery with a diamond-shaped patch, and your neck is sown shut
- carotid angioplasty: a thin tube called a catheter is threaded from your femoral artery up to the narrowing; a balloon at the end of the catheter is then inflated, mashing the plaque into the artery wall and expanding a stent
To treat aneurysms, the portion of your artery that's affected is removed and replaced with a graft. Sometimes, a stent graft is placed into the affected area to relieve most of the pressure of blood flowing through the aneurysm to prevent rupture.
As with any medical procedure, results vary from patient to patient, depending on age, genetics, condition severity, as well as environmental and health factors. Consult your healthcare practitioner before embarking on your treatment journey.
Reserve Your Appointment Now
Vasculitis can be a painful and life-threatening condition. Getting medical attention is vital if you suspect you're experiencing vasculitis. To speak with a vasculitis specialist today in Pelican Bay - Naples, call (941) 845-6555 or contact Dr. Nancy Vance online.
Sources:
1. Ponte, Cristina et al. "Giant Cell Arteritis: Current Treatment and Management." World Journal of Clinical Cases : WJCC 3.6 (2015): 484–494. PMC. Web. 27 July 2018.
2. Daikeler, Thomas & Koetter, Ina & Bocelli Tyndall, Chiara & Apperley, Jane & Attarbaschi, Andishe & Guardiola, Philippe & Gratwohl, Alois & Jantunen, Esa & Marmont, Alberto & Porretto, Ferdinando & Musso, Maurizio & Maurer, Britta & Rinaldi, Nadia & Saccardi, Riccardo & Tyndall, Alan. (2007). Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for vasculitis including Behçet's disease and polychondritis: A retrospective analysis of patients recorded in the European Bone Marrow Transplantation and European League Against Rheumatism databases and a review of the literature. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 66. 202-7. 10.1136/ard.2006.056630.
Insight to Health & Wellness, Inc.
Address
694 8th Street NorthNaples, FL 34102
(941) 845-6555
www.insight2hw.com


